Fairness-aware Data Integration
- Collaboration:
- This is a joint project with Dr. Nargesian and Dr. Jagadish.
- Publications:
- [1] Fatemeh Nargesian, Abolfazl Asudeh, H. V. Jagadish. Tailoring Data Source Distributions for Fairness-aware Data Integration. VLDB, Vol. 14(11), pages 2519--2532, 2021, VLDB Endowment.
- [2] (Tutorial) Fatemeh Nargesian, Abolfazl Asudeh, H. V. Jagadish. Responsible Data Integration: Next-generation Challenges. In proceedings of the 2022 International Conference on Management of Data (SIGMOD '22), June 12--17, 2022, Philadelphia, PA, USA. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1145/3514221.3522567
- Abstract:
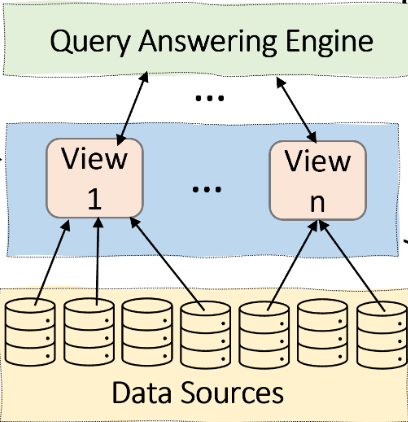
- Data integration has been extensively studied by the data management community and is a core task in the data pre-processing step of ML pipelines. When the integrated data is used for analysis and model training, responsible data science requires addressing concerns about data quality and bias. We present a tutorial on data integration and responsibility, highlighting the existing efforts in responsible data integration along with research opportunities and challenges. We encourage the community to audit data integration tasks with responsibility measures and develop integration techniques that optimize the requirements of responsible data science. We focus on three critical aspects: (1) the requirements to be considered for evaluating and auditing data integration tasks for quality and bias; (2) the data integration tasks that elicit attention to data responsibility measures and methods to satisfy these requirements; and, (3) techniques, tasks, and open problems in data integration that help achieve data responsibility.
AI technologies provide user-friendly solutions at a scale and efficiency that was not imaginable before. In decision making, AI can help to eliminate human bias, and to make wise decisions that benefit human beings and societies. Its many benefits have caused the AI revolution to have a huge impact on all aspects of modern human life. As AI is fusing into our lives, its potential harms have become more evident. We all have perhaps faced or heard many of these concerns. The concept of Responsible AI has been introduced to minimize the drawbacks of AI.
It is known that AI is as good as the data it is built on. When data does not contain enough signals to address business needs, no model can achieve a high-enough performance to address those needs, hence, responsible AI requires that responsible data be collected. Since responsible data is often scattered across multiple sources, responsible data integration is required for collecting the responsible data. Consider the following example in the healthcare domain.
Responsible AI introduces new challenges and requirements for data integration, that require revisiting different tasks in the pipeline of data integration to make sure these needs are satisfied.