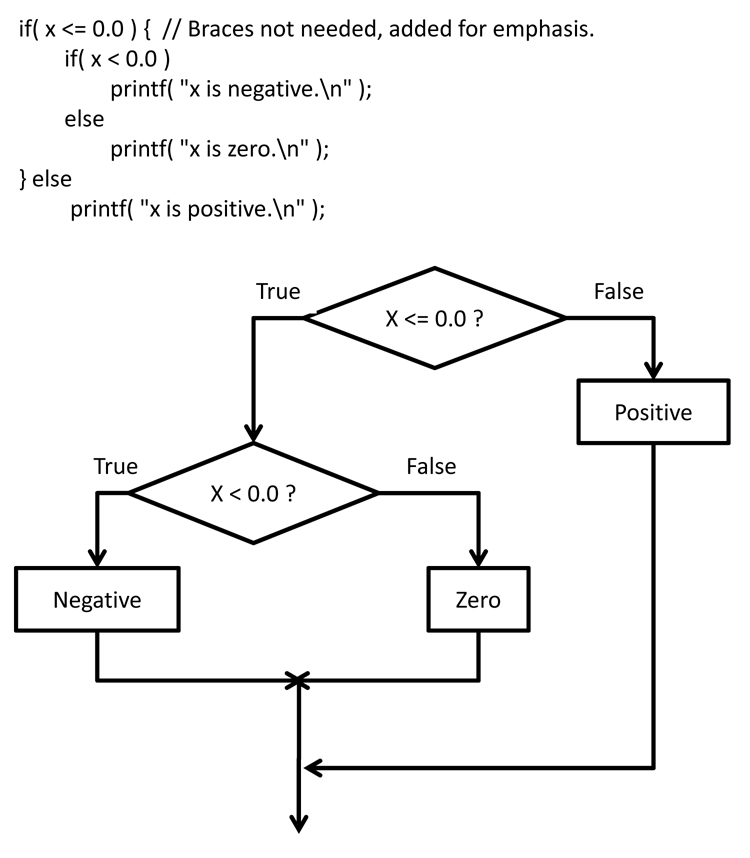
if( condition )
true_block
else
false_block
- If the condition evaluates to true ( non-zero ), then the true_block of code is executed.
- If the condition evaluates to false ( zero ), then the false-block of code is executed if it is present.
- After one or the other block is executed, then execution continues with whatever code follows the if-else construct, without executing the other block.
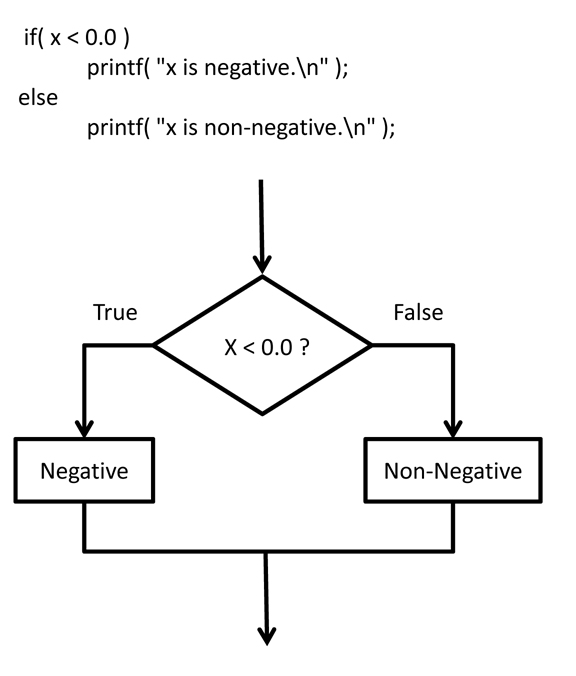
if( x < 0.0 ) {
printf( "Error - The x coordinate cannot be negative. ( x = %f ) \n", x );
exit( -1 );
}
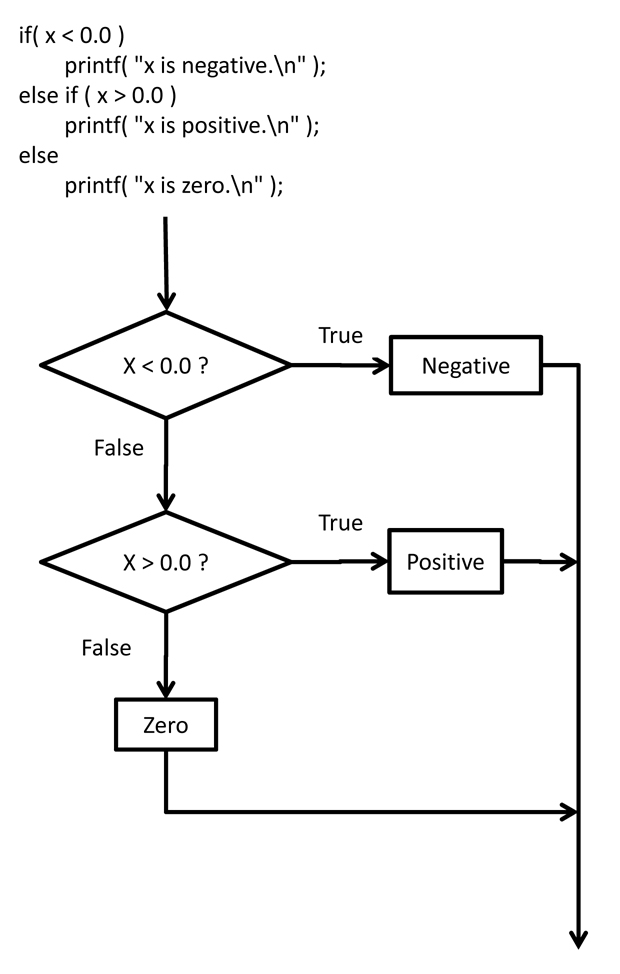
- When an if-else construct is used in the true block of another if-else, that is termed nested ifs.